008613968780263
008613968780263 0102030405
Aluminum Heat Sink: The Unsung Hero of Electronic Cooling
2025-10-07
In the fast-paced world of electronics, where devices are becoming smaller, more powerful, and more compact, heat management has emerged as a critical challenge. Excess heat can degrade performance, shorten the lifespan of components, and even cause sudden failures. This is where the Aluminum Heat Sink steps in as an unsung hero, quietly ensuring that our smartphones, laptops, LED lights, and industrial machines operate smoothly.
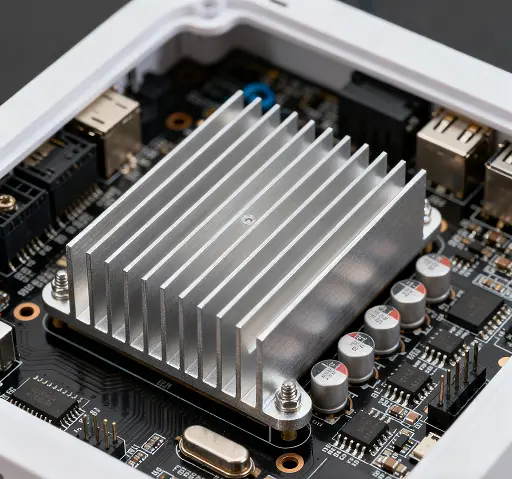
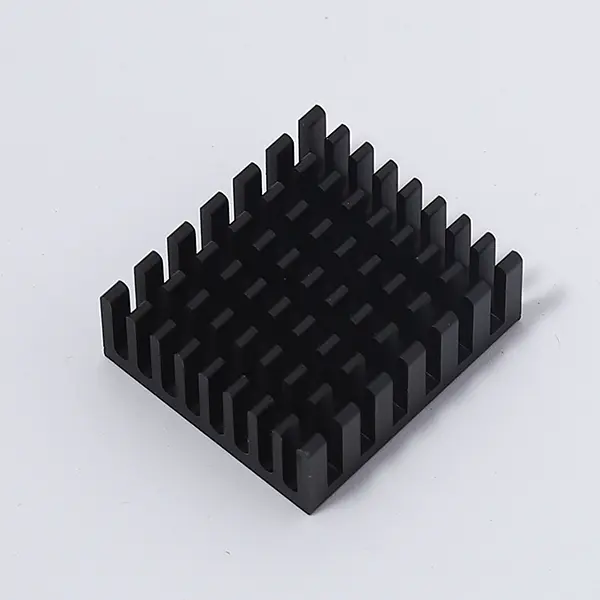
What makes aluminum the material of choice for heat sinks? First and foremost is its exceptional thermal conductivity. While not as high as copper, aluminum offers a perfect balance of performance, cost-effectiveness, and lightweight properties. A typical Aluminum Heat Sink can efficiently absorb heat from electronic components (such as microchips or power transistors) and dissipate it into the surrounding air, preventing overheating. Additionally, aluminum is highly malleable, allowing manufacturers to design heat sinks in diverse shapes—from simple extruded fins to complex 3D-printed structures—that maximize surface area for better heat transfer.
The applications of Aluminum Heat Sink are widespread across industries. In consumer electronics, they are found in gaming laptops, where high-performance GPUs generate massive heat, and in smartphones, where space constraints demand compact yet efficient cooling solutions. In the automotive sector, they cool electric vehicle (EV) batteries and power electronics, ensuring safe and reliable operation. Even in household items like LED bulbs, Aluminum Heat Sink play a vital role: LEDs produce less heat than traditional bulbs, but their longevity still depends on keeping temperatures low. Without a heat sink, an LED bulb’s lifespan could be cut in half.
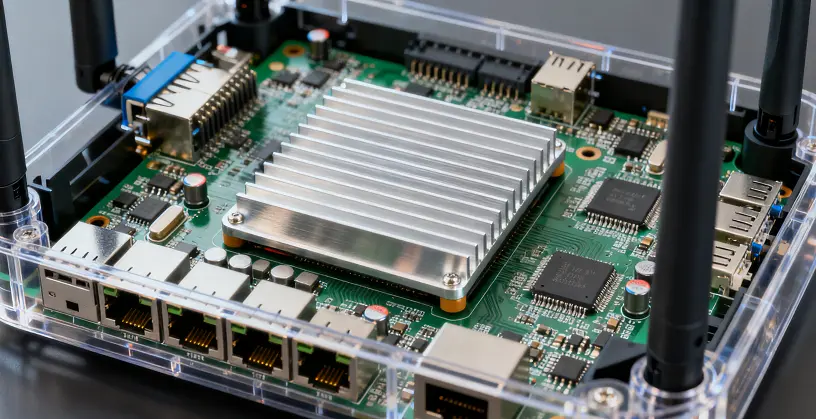


As technology advances, the design of Aluminum Heat Sink continues to evolve. Engineers are now integrating heat pipes or vapor chambers with aluminum heat sinks to enhance cooling efficiency, especially for high-power devices. Surface treatments, such as anodization, not only improve corrosion resistance but also increase emissivity, helping the heat sink radiate heat more effectively. These innovations ensure that Aluminum Heat Sink remain relevant in an era of ever-more powerful electronics.
In conclusion, while Aluminum Heat Sink may not be the most visible component in our devices, their role in maintaining performance and reliability is indispensable. As electronics continue to advance, the demand for innovative, efficient aluminum heat sink solutions will only grow—solidifying their place as a cornerstone of modern technology.