008613968780263
008613968780263 New Trends in Switch Cooling Fan Development
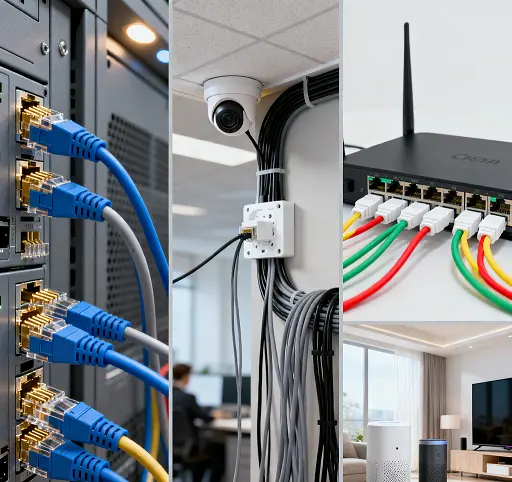
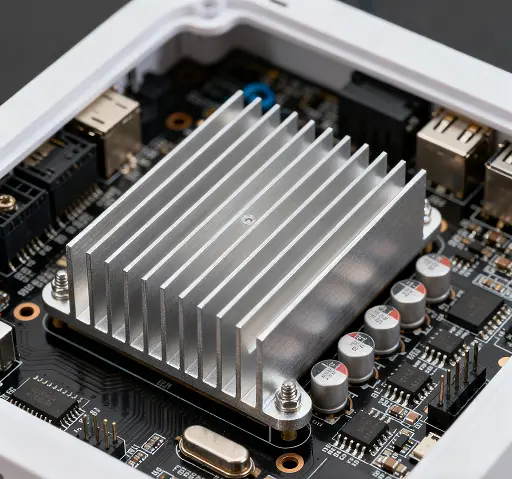
In the digital age, switches, as the core equipment of network communication, have witnessed a development process of their heat sinks, which is a vivid illustration of technological progress.
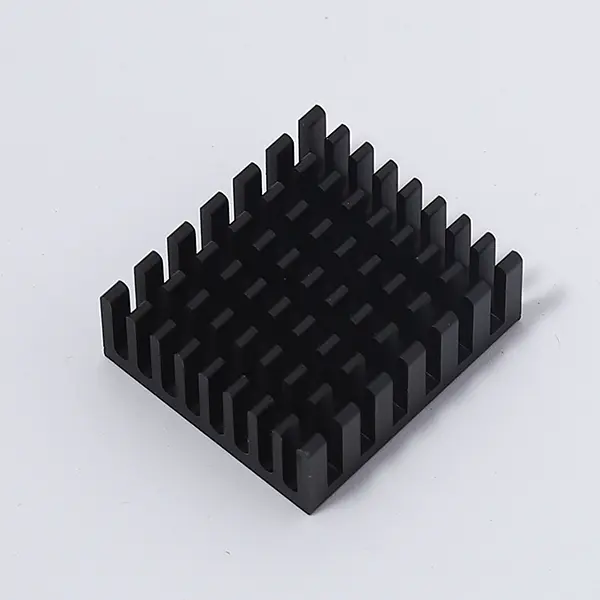
In the early days, the structure of heat sinks was simple and mostly made of metal. The heat dissipation efficiency could not meet the increasing demands of equipment. With the advancement of technology, the design of heat sinks has become increasingly sophisticated. Nowadays, multi-fin structure and micro-channel technology are widely used, significantly increasing the heat dissipation area and enhancing the heat dissipation efficiency. The introduction of new materials has also provided new impetus for the development of heat sinks. Graphene composite materials, for example, not only have excellent heat dissipation performance but also possess lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties, effectively reducing the weight of equipment and maintenance costs.
The emergence of intelligent cooling technology has made heat sinks more "intelligent". Through built-in sensors, the heat sinks can monitor the operating temperature of the switch in real time and automatically adjust the cooling intensity to achieve on-demand cooling. This not only ensures the stable operation of the equipment but also significantly reduces energy consumption. In large-scale application scenarios such as data centers, the application of this intelligent heat sink has greatly improved the reliability and operational efficiency of the equipment.
In the future, with the deep integration of technologies such as 5G and artificial intelligence, the performance requirements for switches will continue to increase, and heat sink technology will also undergo continuous innovation, moving towards higher efficiency, greater intelligence, and greater environmental friendliness, providing a solid guarantee for the stability and efficiency of network communication.